Bitcoin’s Inflation Hedge Story: BTC Reacts More to Dollar Drops
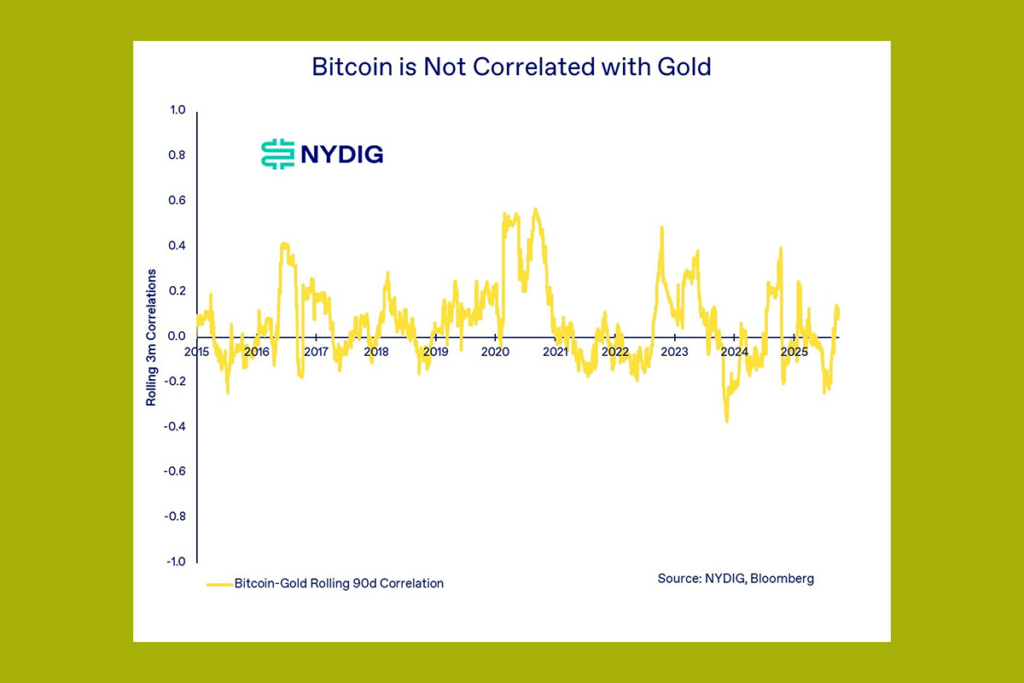
NYDIG claims that inflation has less of an effect on the price of Bitcoin than most people think. However, the cryptocurrency tends to rise in tandem with gold when the US dollar declines.
The community likes to pitch Bitcoin as an inflation hedge, but unfortunately, here, the data is just not strongly supportive of that argument. The correlations with inflationary measures are neither consistent nor are they extremely high,
NYDIG global head of research Greg Cipolaro
According to Cipolaro, inflation expectations are a more accurate indicator of Bitcoin, although they are still not highly correlated.
Analyst: Bitcoin and Gold Both Gain When the Dollar Declines
Because of its hard-limited quantity and decentralized nature, Bitcoin proponents have long praised the cryptocurrency as digital gold and a hedge against inflation. However, it has become increasingly integrated and linked to the conventional financial system lately. According to Cipolaro, real gold is not a particularly effective inflation hedge. He went on to say that it is inconsistent across time periods and has an inverse relationship with inflation. This is unexpected for an inflation hedge, he noted. According to him, when the US dollar has declined in value relative to other currencies, using the US Dollar Index, gold has generally increased.
Bitcoin also has an inverse correlation to the US dollar. While the relationship is a bit less consistent and newer than gold’s, the trend is there.
Cipolaro
Bitcoin Becoming More Integrated Into Global Markets Like Gold
According to Cipolaro, the money supply and interest rates were the two primary macroeconomic variables that influenced the prices of gold and Bitcoin. Generally speaking, gold has increased when interest rates have decreased and decreased when they have increased. He believes that Bitcoin has also developed and grown stronger over time. According to him, given specific macroeconomic circumstances, the price oscillations of Bitcoin are starting to resemble those of gold. He continued by saying that this illustrates how Bitcoin is becoming more and more integrated into the world’s financial and monetary system.
If we were to summarize how to think about each asset from a macro factor perspective, it is that gold serves as a real-rate hedge, whereas Bitcoin has evolved into a liquidity barometer,
Cipolaro
For more up-to-date crypto news, you can follow Crypto Data Space.


































Comments are closed.