Understanding Bitcoin’s Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs)
Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs) are integral to Bitcoin’s unique design, serving as discrete pieces of the cryptocurrency that can be combined and split to facilitate transactions of any denomination.
Analogous to physical coins, UTXOs must be spent discretely, meaning you cannot spend a portion of a UTXO. Instead, you spend the entire UTXO and receive change if necessary. Unlike physical coins, UTXOs don’t adhere to standardized denominations, allowing them to hold any amount of bitcoin.
UTXOs result from the outputs of Bitcoin transactions and exist as unspent until used as inputs in subsequent transactions. Bitcoin nodes maintain the UTXO set, which encompasses all existing UTXOs, ensuring transparency and addressing the Double Spend Problem, a challenge faced by earlier digital currency attempts.
Creation of UTXOs primarily occurs through coinbase transactions. These transactions are unique as they generate new bitcoins as rewards for block miners, creating new UTXOs in the process. The coinbase transaction has no inputs and one or more outputs, all of which become new UTXOs.
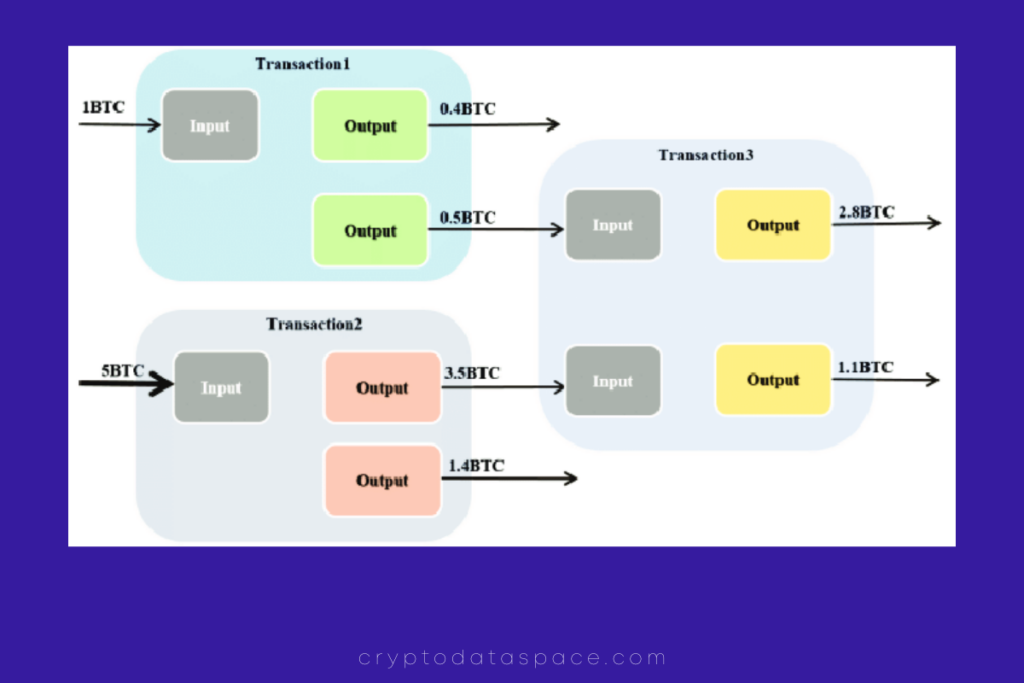
Bitcoin’s UTXO model distinguishes itself from traditional financial systems, aiming to be transparent, fair, and auditable. Instead of accounts, Bitcoin transactions involve addresses that receive UTXOs. However, addresses aren’t directly inscribed on the blockchain; they are encodings of scriptPubKeys found in transaction outputs. The previous address of a UTXO can be deduced by referencing the previous transaction’s id and the output index.
The UTXO model allows for precise auditing of Bitcoin’s total supply, ensuring compliance with its monetary policy. Transactions can contain multiple inputs and outputs, facilitating the combination and splitting of UTXOs to enable payments of any amount. Transaction verification is efficient as nodes can verify the validity and unspent status of UTXOs, negating the need for trusted third parties and solving the Double Spend Problem.
In contrast to the UTXO model, most financial systems and cryptocurrencies use the accounts model. With the accounts model, individuals hold balances within specific accounts, enabling precise debiting and crediting without the need for coin selection or change considerations.
Overall, the UTXO model remains a fundamental aspect of Bitcoin’s design, empowering its decentralized nature and supporting its auditable and transparent monetary system.
















Leave a comment