Understanding Decentralized Identity: Redefining Digital Identity Management with Blockchain
Decentralized identity is a groundbreaking method of digital identity management that restores individual control and eliminates dependency on centralized institutions such as governments, businesses, or identity providers. Decentralized identification uses blockchain technology to provide consumers ownership and control over their identity without relying on third parties, in contrast to traditional identity systems that hold personal data through intermediaries.
Users regain control through decentralized identities. Blockchain technology allows people to safely handle, exchange, and validate their personal information in a self-sovereign manner, guaranteeing increased security and privacy. This solution provides a more secure option to conventional identity management by preventing unwanted access to private data and reducing the likelihood of data breaches.
In both the digital and physical spheres, identity is essential because it dictates how we use services, take advantage of opportunities, and defend our rights. Decentralized identity gives individuals the ability to take back control of their data and protect their online presence, which is crucial in the digital world where personal information is extremely valuable.
Decentralized Identity Systems: Protecting Personal Data in the Digital Age
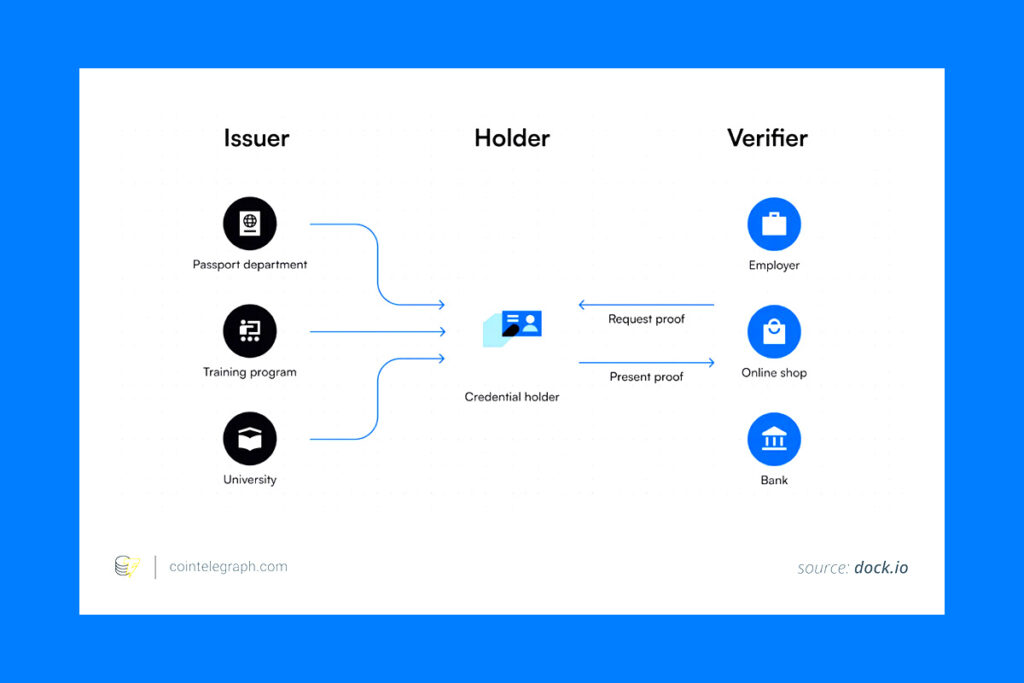
Blockchain technology is utilized by decentralized identification systems to provide a safe and user-friendly foundation for digital identity management. These solutions guarantee data security and privacy while empowering people to take charge of their personal information.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs), Verifiable Credentials (VCs), and Identity Wallets are the three fundamental elements that make up decentralized identity. DIDs are distinct identifiers that are kept on the blockchain and protect privacy by preventing direct connections to private information. VCs serve as safe digital copies of conventional papers, such as certificates or passports, that let users exchange particular information without disclosing extraneous details. Identity wallets are digital storage solutions that help users maintain their VCs, establish DIDs, and restrict who can access their data.
The Holder, Issuer, and Verifier are the three main players in the decentralized identification system. The person who creates a DID and obtains a verifiable credential is known as the holder. The credential is digitally signed and provided by the issuer, a reliable organization. In contrast, the verifier uses the issuer’s public DID on the blockchain to verify the credential’s legitimacy.
The holder demonstrates identity ownership using cryptographic techniques without disclosing private information. They create a safe proof by signing their data with a private key, which the verifier verifies with the matching public key. This simplified procedure protects the confidentiality of the holder’s private information while guaranteeing the accuracy of the data.
Key Benefits and Limitations of Blockchain-Powered Decentralized Identity Systems
Blockchain-based decentralized identity provides a revolutionary approach to digital identity management with several advantages. This approach improves privacy and autonomy by giving people control over their personal data and ensuring that it is shared only when required. The unchangeable ledger and cryptography used by blockchain greatly lower the possibility of identity theft and data breaches, establishing a safe environment for online communication. Additionally, decentralized identities facilitate smooth platform interoperability, streamlining verification procedures and cutting costs for enterprises and individuals alike.
Decentralized identification has shortcomings that must be addressed before it can be widely used, despite its benefits. Resistance is frequently generated when switching from old systems since it necessitates significant changes in user behavior and infrastructure. Regulatory compliance increases complexity because these systems have to adhere to stringent regulatory requirements, especially with frameworks like GDPR. The administration of keys is still a significant obstacle; users have a great deal of responsibility since losing a private key could result in the permanent loss of access to a digital identity. Decentralized identification systems’ performance may also be hampered by blockchain scalability problems, particularly as transaction volumes increase.
The Future of Decentralized Identity: Transforming Digital Footprints in Web3
As adoption picks up speed and technological developments continue to transform the digital landscape, the future of decentralized identity seems bright. Decentralized identification, which gives people more control over their digital footprints, is essential to creating a private and secure Web3 ecosystem. Leading sectors, including finance, healthcare, and education, are leading the way in integrating blockchain-based identity solutions to streamline identity management and enhance privacy and security.
Decentralized identification systems may now seamlessly connect across platforms and effectively handle growing demands thanks to advancements in blockchain technology that are tackling important challenges like scalability and interoperability. These advancements are essential for encouraging broad acceptance and guaranteeing an easy-to-use interface.
For more up-to-date crypto news, you can follow Crypto Data Space.















Leave a comment