Master Margin Trading
Take your crypto trading skills to the next level by mastering margin trading. This dynamic trading method allows you to leverage market movements (whether bullish or bearish) while navigating associated risks.
Margin trading in crypto involves borrowing funds (leverage) to increase your market exposure, enabling traders to magnify potential returns. In this guide, you’ll learn the basics of margin trading, explore the mechanics of long and short positions, and discover platforms that support this advanced trading strategy.
Understanding Long and Short Positions
Long Positions
A long position involves purchasing an asset (such as cryptocurrencies or stocks) with the expectation that its price will rise. Traders profit by buying low and selling high, capitalizing on the difference. This approach is typically used in bullish markets where asset values are anticipated to increase.
Short Positions
Short-selling, or taking a short position, is the inverse strategy. Traders sell borrowed assets expecting a price drop. They later repurchase the assets at a lower price, returning them to the lender and pocketing the difference as profit. This tactic thrives in bearish markets and is based on a negative price outlook.
Key Difference
While both strategies aim to profit from market movements, the approach and risks differ. Long positions are optimized for rising markets, while short positions capitalize on declines.
The Mechanics of Margin Trading
Margin trading involves borrowing funds from a broker or platform to amplify your trading position. By using leverage, you can control a larger amount of capital than you own, but this also increases both potential gains and losses.
Collateral and Maintenance Margin
To trade on margin, you must deposit collateral, which could be fiat currency, stablecoins, or cryptocurrencies. A maintenance margin is the minimum equity you need to hold to avoid a margin call, where the platform may liquidate your assets to cover losses.
Risk Amplification
While margin trading can enhance profits, it also magnifies losses, making robust risk management crucial. Mastery of market dynamics and risk strategies is essential to succeed in this high-stakes arena.
Identifying Margin Trading Opportunities
To identify the right moments to go long or short with margin trading, traders can employ technical analysis and market sentiment analysis:
- Technical Tools: Use indicators such as moving averages, momentum oscillators, and support/resistance levels.
- Market Sentiment: Monitor news, social media trends, and analyst reports for shifts in investor behavior.
- Shorting Opportunities: Look for overvalued assets or weakening technical patterns. Pay attention to macroeconomic factors like interest rate changes or geopolitical developments.
- Longing Opportunities: Identify undervalued assets with strong growth potential. Analyze earnings reports, market trends, and technological innovations.
How to Long and Short Crypto with Margin Trading
Longing Crypto
- Select a Platform
Choose a reputable margin trading platform like Binance, Kraken, or a DeFi protocol such as Aave. - Create and Fund an Account
Complete KYC requirements and deposit funds to meet margin requirements. - Choose Account Type
Opt for isolated margin (allocates funds to specific trades) or cross-margin (uses the entire account balance as collateral). - Provide Collateral
Deposit the required collateral and select an appropriate leverage ratio (e.g., 2x, 5x, or 10x). - Place a Long Order
After setting up collateral and leverage, initiate a long position. Input the desired quantity and specifications. - Close the Position and Withdraw Profits
Sell the asset at a higher price to repay the borrowed amount and interest. Transfer any profit to your wallet or bank account.
Shorting Crypto
- Select a Platform
Pick a platform with strong margin trading features, such as BitMEX or Interactive Brokers. - Create and Fund an Account
Set up the account, verify identity, and deposit funds to meet margin requirements. - Choose Account Type
Decide between cross-margin or isolated margin trading options. - Provide Collateral
Deposit collateral and determine a leverage ratio aligned with your strategy. - Place a Short Order
Sell borrowed cryptocurrency with the expectation of repurchasing it at a lower price. Finalize the order details. - Close the Position and Collect Profits
Repurchase the cryptocurrency at a lower price to return the borrowed amount. Withdraw your earnings.
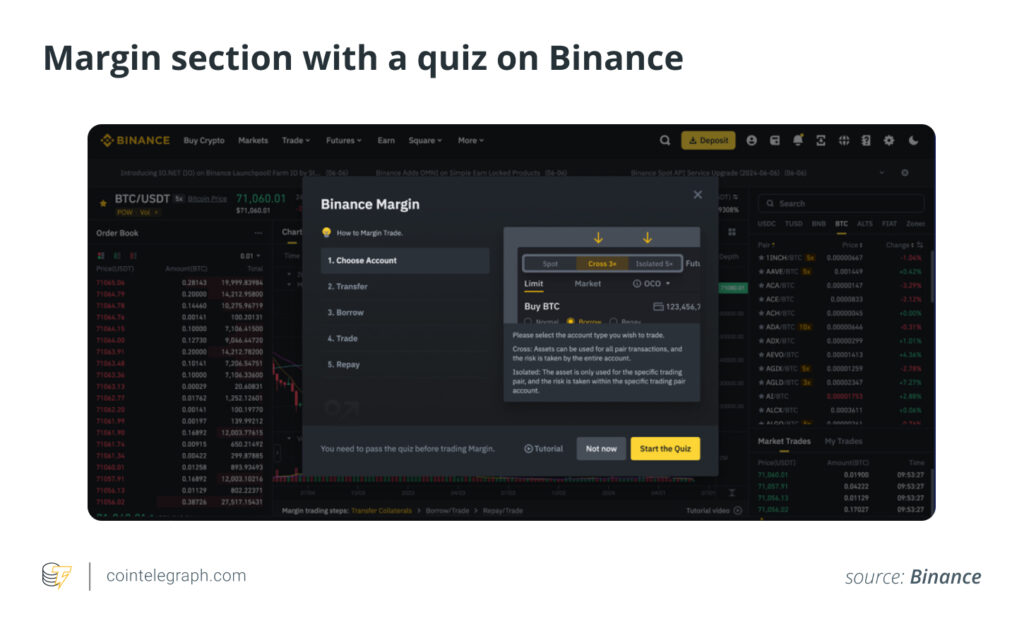
Costs and Fees in Margin Trading
Transaction Fees
Exchanges often charge maker (providing liquidity) and taker (removing liquidity) fees.
Margin Fees
Daily margin rates vary based on market conditions.
Withdrawal and Swap Fees
DeFi platforms may charge gas fees, liquidity provider fees, or fluctuating interest rates for borrowing.
Tax Implications of Margin Trading
Capital Gains Tax
Profits from margin trading are subject to capital gains tax, varying by jurisdiction and holding period. Short-term gains typically incur higher rates than long-term gains.
Forced Liquidations and Margin Calls
Gains or losses from forced liquidations may also be taxed, while margin calls themselves are not taxable events unless they lead to asset sales.
Risk Management for Margin Trading
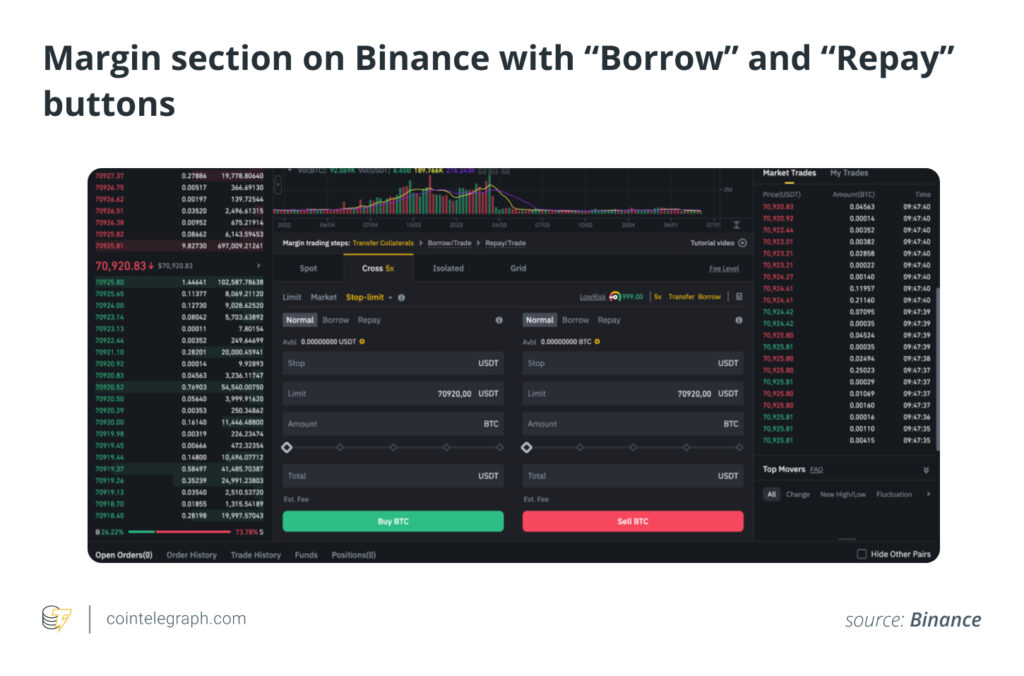
Effective risk management is critical in margin trading:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Use stop-loss orders to limit downside risks. Place them above resistance levels for shorts or below support levels for longs.
- Monitor Margin Levels: Keep an eye on collateral levels to avoid margin calls.
- Liquidation Awareness: Understand liquidation thresholds to preempt excessive losses.
Conclusion
Margin trading unlocks significant opportunities to profit from market volatility, but it requires expertise, discipline, and thorough risk management. By mastering long and short positions and understanding the mechanics of leveraged trading, traders can enhance their strategies while mitigating risks. Explore reputable platforms, fine-tune your approach, and elevate your crypto trading game.















Leave a comment