Understanding the Intrinsic Value of Cryptocurrencies
Intrinsic value refers to the actual worth of an asset based on its fundamental attributes rather than its market price. In traditional finance, this concept often revolves around earnings, cash flow, and growth potential. However, determining the intrinsic value of cryptocurrencies is far more complex due to their unique nature. Unlike stocks, cryptocurrencies lack ties to physical assets or consistent income streams, such as dividends.
Instead, their intrinsic value hinges on a combination of technological, economic, and utility-driven factors. At its core, intrinsic value answers the question: What makes this cryptocurrency valuable beyond its exchange price?
Factors Influencing Cryptocurrency Intrinsic Value
Cryptocurrencies derive their intrinsic value from various characteristics, such as:
- Utility: What problems does the cryptocurrency address?
- Scarcity: Is its supply finite or inflationary?
- Network Value: How large and active is the ecosystem?
- Security: How robust is the blockchain against potential attacks?
For instance, Bitcoin draws its value from its limited supply (capped at 21 million coins), decentralized structure, and secure proof-of-work (PoW) consensus. Ethereum, on the other hand, gains value as the foundation for decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts.
Methods for Calculating Intrinsic Value
Several methods are commonly employed to estimate the intrinsic value of cryptocurrencies. Here are three popular approaches:
1. Metcalfe’s Law
- Overview: Metcalfe’s Law posits that the value of a network is proportional to the square of its active users. In essence, as the number of users increases, the network’s value grows exponentially.
- Application: This method is ideal for cryptocurrencies with robust ecosystems and active user bases.
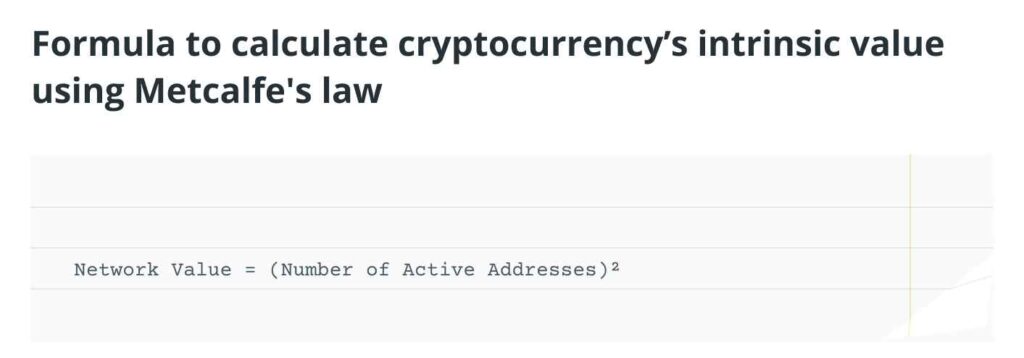
Example: Ethereum
Ethereum hosts a vast network of developers and millions of active users. The number of daily active addresses can serve as a proxy for its network size.
As of December 13, 2024, Ethereum reported 543,929 daily active addresses. Using Metcalfe’s Law: Network value=(Active users)2=543,9292=296,086,104,841\text{Network value} = (\text{Active users})^2 = 543,929^2 = 296,086,104,841Network value=(Active users)2=543,9292=296,086,104,841
This exponential growth underscores the potential of a thriving user network. However, Metcalfe’s Law has its limitations:
- It overlooks the quality of user interactions.
- Estimating active users can be challenging due to bot activity.
- It doesn’t account for technological differentiators like transaction speed.
2. Cost of Production
- Overview: This approach calculates intrinsic value based on production or mining costs. For PoW cryptocurrencies, this includes energy, hardware, and operational expenses.
- Application: Production costs act as a “price floor” because miners typically stop operations if market prices fall below these costs.
Example: Bitcoin Bitcoin’s intrinsic value often correlates with its mining cost. For instance:
- As of December 13, 2024, Bitcoin’s average mining cost was $86,303, while its market price stood at $101,523. This $15,220 surplus highlights profitability and ensures network security.
- During bearish markets, prices can dip below mining costs, causing inefficiencies and potentially impacting security.
Challenges:
- Mining costs vary globally, influenced by energy prices and local regulations.
- Market volatility may temporarily decouple prices from production costs.
3. Discounted Utility Model
- Overview: This method estimates intrinsic value by projecting a cryptocurrency’s future utility, such as transaction volume or adoption rates, and discounting it to present-day value.
- Application: Analysts assess potential adoption scenarios and calculate the discounted value of future benefits.
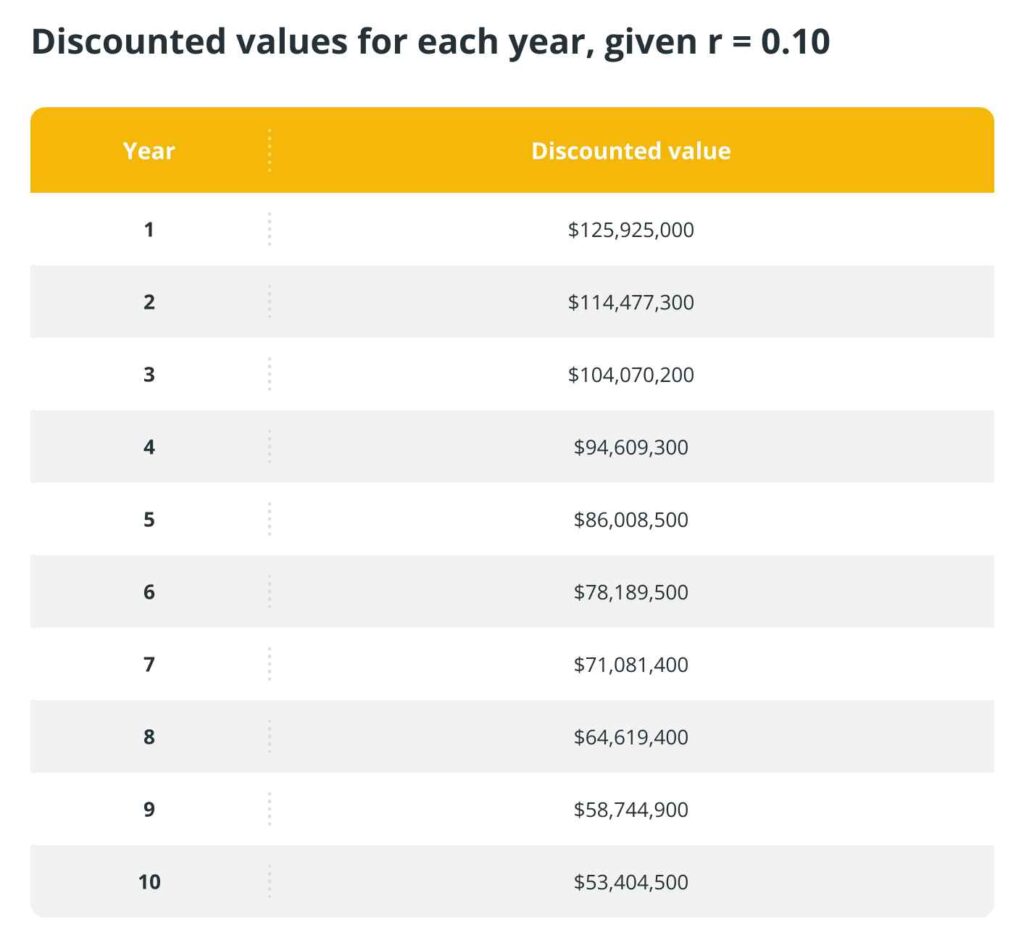
Example: BNB
BNB derives its value from its utility within the Binance ecosystem. It facilitates fee payments, token sales, and staking rewards. Assuming Binance Smart Chain processes 3.795 million daily transactions with an average fee of $0.10: Daily fees=3,795,000×0.10=$379,500\text{Daily fees} = 3,795,000 \times 0.10 = \$379,500Daily fees=3,795,000×0.10=$379,500 Annual fees=379,500×365=$138.52 million\text{Annual fees} = 379,500 \times 365 = \$138.52 \text{ million}Annual fees=379,500×365=$138.52 million

Using a 10% discount rate over 10 years, the total discounted utility of BNB would approximate $851.13 million.
Challenges:
- Predicting future transaction volumes involves speculation.
- Valuations are highly sensitive to changes in discount rates.
- External factors, such as competition or regulatory challenges, could impact the ecosystem’s utility.
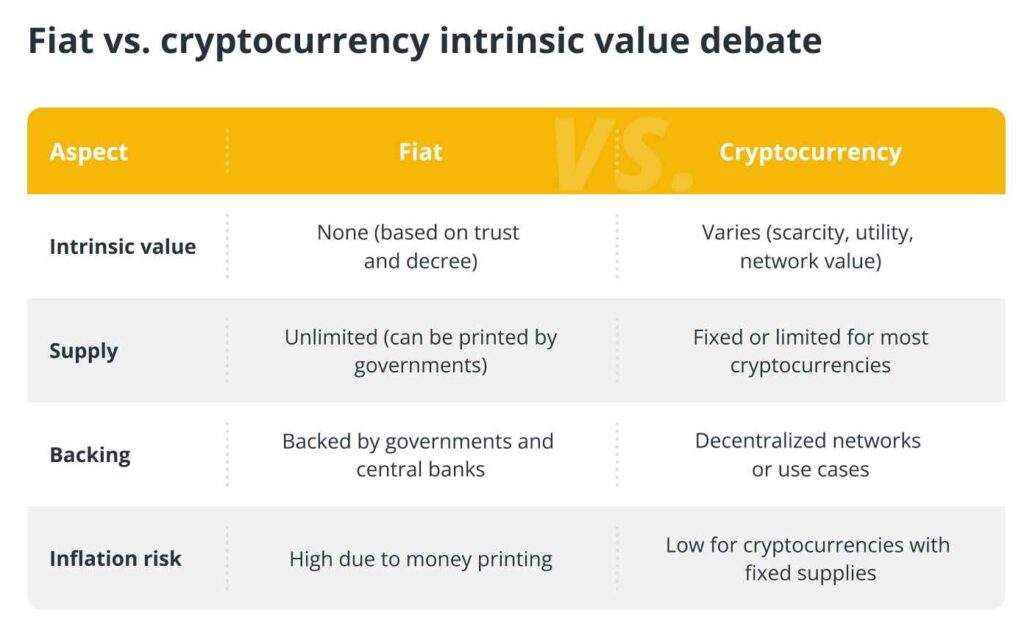
Intrinsic Value of Fiat Currencies
In contrast to cryptocurrencies, fiat currencies lack intrinsic value in the traditional sense. Unlike gold or silver, fiat money isn’t backed by physical commodities. Instead, its value stems from:
- Government decree: Fiat is declared legal tender.
- Trust: The public trusts governments to manage economies responsibly.
- Utility: Fiat is universally accepted, highly liquid, and practical for transactions.
However, fiat currencies are vulnerable to inflation due to their unlimited supply, eroding purchasing power over time.
Why Intrinsic Value Matters
Understanding intrinsic value allows investors to distinguish promising projects from speculative ones. During the 2017 ICO boom, countless tokens with negligible intrinsic value collapsed. Conversely, Bitcoin has demonstrated long-term viability due to its scarcity, network effects, and security.
By evaluating intrinsic value, investors can avoid hype and make informed decisions, focusing on projects with sustainable growth potential.
Final Thoughts
The concept of intrinsic value provides a lens through which to assess cryptocurrencies and fiat. While fiat derives its worth from external trust and governance, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin gain intrinsic value through their inherent properties, such as decentralization and finite supply. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating the evolving financial landscape.















Leave a comment