Travel rule crypto is a concept that has emerged to prevent the malicious use of cryptocurrencies, which are becoming more and more popular every day.
Travel Rule Crypto
As time goes by, cryptocurrencies are becoming more and more embedded in the daily use of human life. Trave rule crypto can be characterized as a measure taken to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing by malicious actors of cryptocurrencies, which are increasing in use. This measure affects everyone in the crypto ecosystem, from exchanges to daily investors.

What is Travel Rule Crypto
In 2019, at the G-7 summit attended by some 30 developed countries, the Financial Action Task Force (an intergovernmental body that initiates anti-money laundering (AML) policies) proposed a coordinated approach called FATF Recommendation #16 to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
This rule required VASPs to transmit information on the originators and beneficiaries of crypto-transactions that exceed a certain limit. More specifically, the regulations require VASPs to exchange information on the identities of the originator and beneficiary of a transaction when the amount traded is over $1,000.

Interpretable
While the travel rule crypto states that ‘for crypto transactions between two parties that exceed $1,000 in value, the crypto service provider of the sender is expected to communicate the personally identifiable information (PII) of the sender to the crypto service provider of the recipient and vice versa’, member states can interpret and localize these guidelines.
For example, in the United States, the crypto travel rule starts at $3,000 (i.e., the rules kick in when the value of a crypto transaction exceeds $3,000). In such cases, VASPs are required to exchange information on the amount traded, the date of movement, and the identity of the crypto service provider. However, another member state may set this limit at $1,000 according to its own living conditions.
Another concrete example is Switzerland is known to have a strict version of the travel rule, where regulators require the identification of private wallets interacting with local VASPs.
FATF’s Recommendations
In addition to the extra information required by individual regulators, FATF recommends the following data ought to be transmitted back and forth by VASPs:
- The names of the sender and the recipient
- The address of the sender
- The account number of the sender and the recipient
Changes in the Travel Rule over Time
In fact, the travel rule existed before the recommendations of the FATF in 2019, but it was aimed at banks and financial institutions. Over time, with the growth of the crypto economy and the increasing use of cryptocurrencies, FATF has tried to adapt these regulations to the crypto area.
In 2019, before the travel rule crypto was published, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in the US was implementing similar practices to VASPs operating in its jurisdiction.
Therefore, the United States did not need a new regulation from scratch to comply with the FATF recommendations. Under this rule, FinCEN requires crypto asset service providers to confirm that crypto transactions do not originate from or are not sent to sanctioned countries or companies.
The Importance of Travel Rule Crypto
As we mentioned at the top of this article, the main purpose of this regulation is to prevent its use by bad actors for malicious purposes. In addition, other reasons why the travel rule crypto is significant are as follows:
- The travel rule ensures that crypto businesses adhere to sanctions.
- It makes it easier for law enforcement to subpoena transaction data.
- It is the first crypto regulation implemented globally, and it could potentially open the door for more uniform crypto regulation.
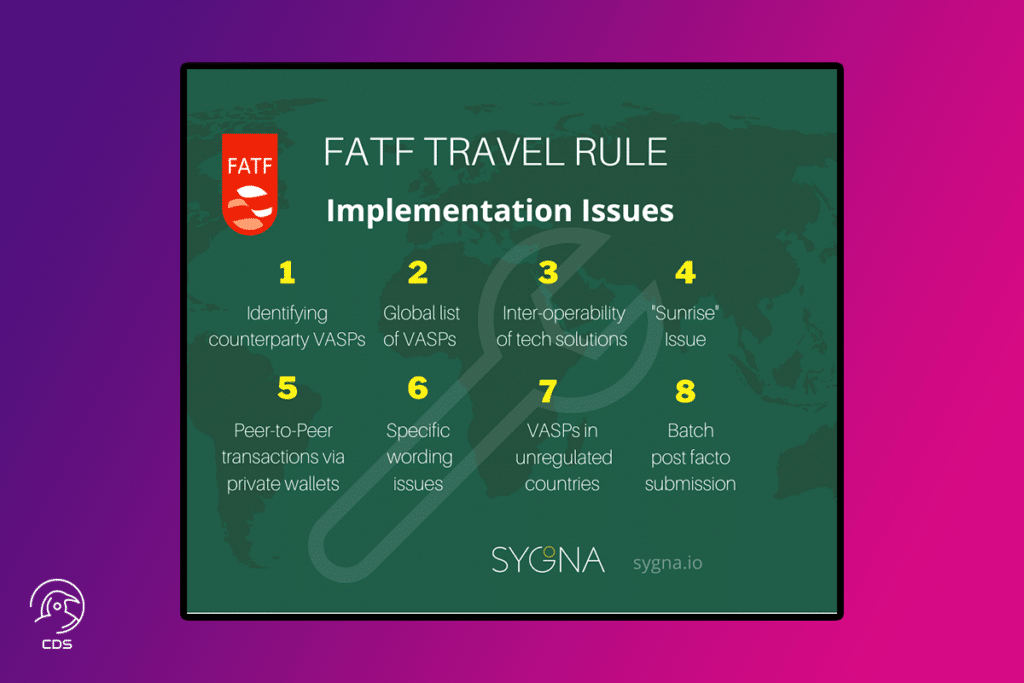
Challenges in Implementation
There are some challenges in the implementation of the Travel Rule. These challenges can be listed as follows:
- Regulations are not so uniform that they cannot be applied in different regions.
- An interoperable communication system is needed for VASPs to easily send and receive PII. This situation means that the entire crypto industry must adopt a collaborative approach to finding the ideal data and communication standards.
- The crypto industry supports a decentralized operating model. Moreover, crypto service providers are coping with this by adopting many protocols specifically designed to help transfer and collect encrypted data. Examples of these protocols are OpenVASP, Shyft, TRISA, and TRP.
The challenges listed above are the main ones, and the list of challenges can be extended.
VISIT OUR OTHER BLOGS: ALL NEWS














Leave a comment