Quant Network is a provider of distributed ledger technology (DLT) services, facilitating the seamless creation of interoperable applications within enterprise systems, which can be interconnected across various blockchains. Gilbert Verdian established the company in 2015, followed by the introduction of its native token, Quant (QNT), shortly thereafter.
Quant Network: A Comprehensive Guide
Quant Network is a service provider for distributed ledger technology (DLT) that empowers enterprise systems to effortlessly construct interoperable applications capable of linking across different blockchains. Shortly after its establishment, Quant Network introduced its native token, Quant (QNT).
Verdian’s profound dedication to enhancing the global exchange of information sparked the inception of the Quant protocol. While serving in governmental roles in both the U.K. and Australia, he recognized the inefficiencies in information exchange and realized the potential of distributed ledger technologies (DLT) to address these challenges.
The Quant protocol stands out as a leading solution to interoperability issues within the blockchain industry. It achieves this by facilitating communication among multiple blockchain platforms through the Overledger DLT Gateway.
This gateway enables interoperability not only between prominent decentralized Layer 1 blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple but also with enterprise-grade blockchains such as ConsenSys Quorum and Hyperledger Fabric.
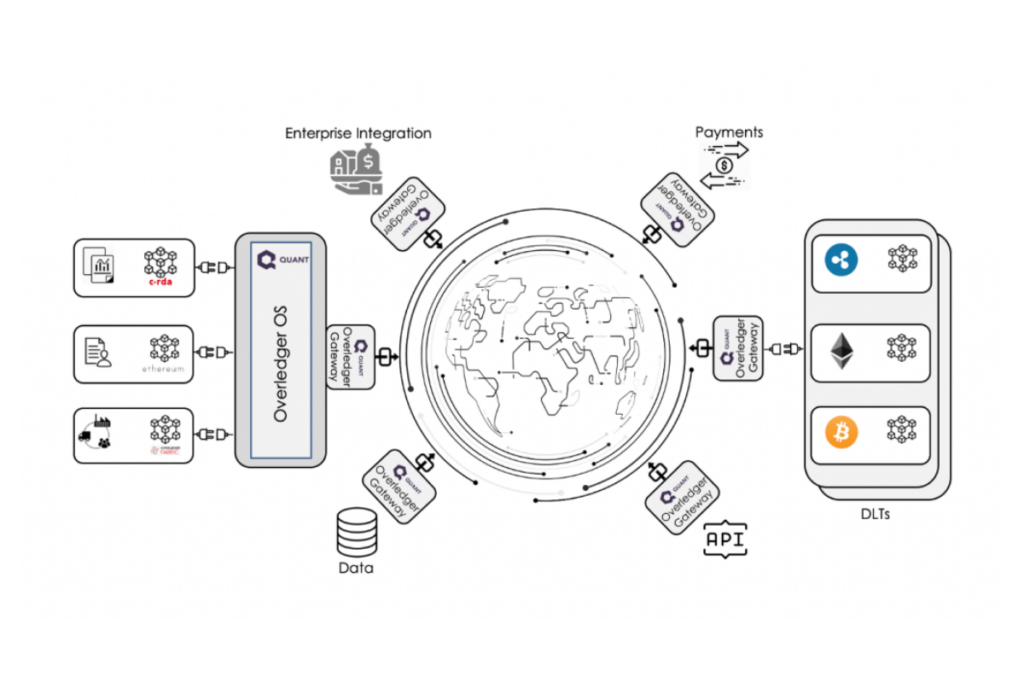
The Quant platform strives to achieve seamless interoperation, aiming to evenly distribute the fragmented landscape of ledger technology. As a result, the Quant protocol is often referred to as an “operating system/software that connects all blockchains.”
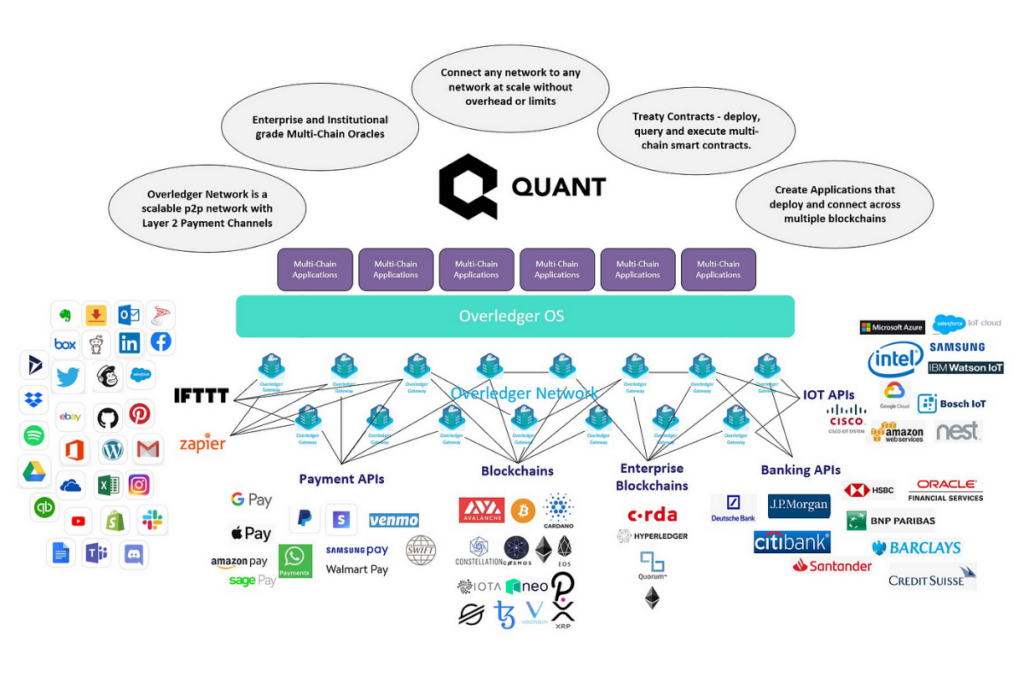
The design of the Quant protocol aims to eliminate common obstacles encountered in communication, interoperability, and scaling within blockchains. To achieve this objective, distinct layers within the network are assigned specific tasks that align with their strengths, as described below.
Transaction Layer: This layer prioritizes the storage of transactions. It utilizes diverse and isolated ledgers to consolidate related operations within a single layer and verify them across the blockchain. Once a transaction is validated, it becomes irrevocable under all circumstances. Consensus mechanisms across blockchains are facilitated within this layer.
Messaging Layer: Information and data transfer are managed in this layer. It processes three types of data: smart contract data, metadata, and transaction data. Metadata assists in interpreting messages and translating them into various languages to ensure compatibility with different blockchains.
Filtering and Ordering Layer: Similar to the messaging layer, this layer handles messages. However, it goes a step further by filtering searches to provide specific results. Every message within the digital ledger system is organized in a chronological order and stored in a database. When off-chain message validation is required, the filtering and ordering layer assumes responsibility, as it retains the message history throughout the protocol.
Application Layer: This final layer governs all other layers by establishing communication rules that all blockchains must adhere to.
By utilizing these four layers, developers can easily assign specific tasks, such as enabling an application to transfer tokens to a specific network once they have developed a decentralized app (DApp).
Quant encompasses several key features that distinguish its platform:
Leveraging the Ethereum Ecosystem: Quant utilizes the Ethereum ecosystem’s security and interoperability by leveraging smart contracts. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily focuses on value transfer, Ethereum offers a broader range of use cases, including decentralized exchanges (DEXs), decentralized finance (DeFi), and blockchain games.
Overledger DLT Gateway: The Overledger DLT Gateway stands as the world’s first blockchain-agnostic API gateway. Its primary purpose is to facilitate interoperability between the distributed ledger system of Quant and other networks. By enabling simultaneous interaction with multiple ledgers, the gateway ensures scalability for decentralized applications (DApps) and multi-DLT applications (mDApps).
Programming Language Flexibility: An exceptional characteristic of Quant’s Overledger DLT Gateway is its capability to allow developers to write smart contracts in any programming language, even on DLTs that do not inherently support them. This flexibility empowers developers by eliminating language restrictions and expanding their options for implementing smart contracts.
Quant (QNT) mDApps: The Quant protocol introduces multi-DLT applications (mDApps) as another unique feature. While traditional DApps typically operate within a single blockchain, mDApps enable different DApps to function across multiple blockchains. With mDApps, developers can take advantage of the unique features and consensus mechanisms of each blockchain without being limited by their individual constraints. This allows developers to leverage consensus from one chain while acquiring data from another, unlocking new possibilities and versatility.
To access more wiki articles: cryptodataspace.com















Leave a comment