Yield farming has become a central concept in the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ecosystem. At its core, yield farming involves depositing cryptocurrency assets into DeFi platforms to earn returns that often outpace traditional investments. Whether you’re a seasoned crypto investor or just starting your journey, yield farming offers an intriguing way to maximize your holdings.
What Is Yield Farming?
Refers to the process of earning returns by locking up crypto assets in liquidity pools or decentralized finance protocols. These returns, which often come in the form of governance tokens or additional cryptocurrencies, reward users for supporting DeFi platforms. Yield farming provides incentives for actions such as providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEXs), staking tokens, or lending assets to money market protocols.
This innovative investment strategy transforms idle crypto assets into revenue-generating tools, but it is not without risks. From impermanent loss to smart contract vulnerabilities, yield farming demands a comprehensive understanding of its mechanisms and associated challenges.
Understanding Yield Farming
Yield farming is often seen as a way to capitalize on the high-yield opportunities available within the DeFi market. It rewards users for their active participation in protocols that contribute to the ecosystem’s growth. Some of the primary roles in yield farming include:
- Liquidity Providers: Contribute funds to liquidity pools on platforms like Uniswap.
- Lenders: Loan their assets to money market platforms like AAVE and earn interest.
- Stakers: Secure blockchain networks by locking up tokens in proof-of-stake protocols.
- Borrowers: Use one token as collateral to borrow another, amplifying their yield potential.
Yield farming rewards generally come from transaction fees, interest, or governance tokens. However, these benefits often mirror the level of risk involved.
The Evolution of Yield Farming
DeFi Summer 2020: The Birth of a Movement
Gained mainstream attention during “DeFi Summer” in 2020. Platforms like Uniswap, Compound, and AAVE became synonymous with the rise of decentralized finance. Governance tokens served as a lucrative incentive for users, marking the first wave of interest in passive income opportunities through crypto.
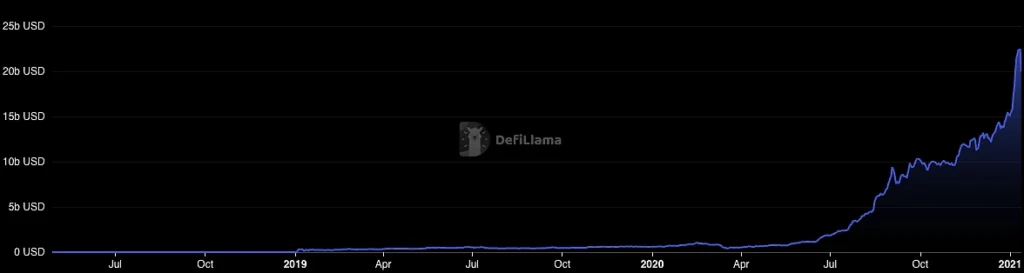
2022 Terra Luna Collapse: A Market Reckoning
The collapse of Terra Luna in 2022 served as a wake-up call. The unsustainable yields promised by platforms like Anchor Protocol, which offered 20% APY on stablecoins, triggered a decline in trust across the DeFi space. This event shifted the focus from inflated returns to more sustainable and realistic yield farming practices.
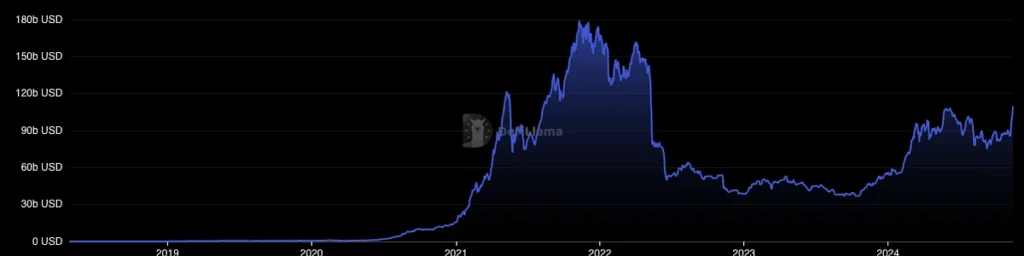
2023 Airdrop Mania: A New Era of Incentives
In the wake of diminishing governance token rewards, crypto projects began embracing airdrop farming. By participating in ecosystem tasks such as bridging tokens or executing trades, users positioned themselves for lucrative token airdrops. Layer 2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum exemplified this trend, sparking renewed interest in decentralized finance.
How Yield Farming Works
Yield farming operates on the principle of liquidity pools. Users deposit tokens into these pools, which are managed through automated smart contracts. Here’s how it works:
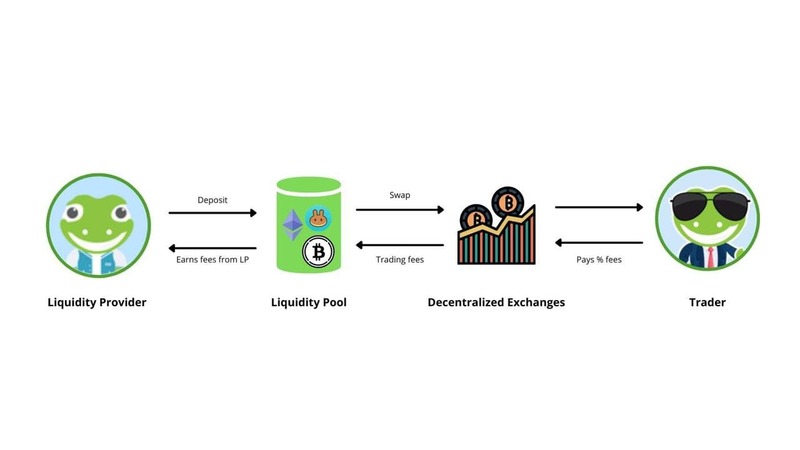
- Liquidity Provision: Crypto assets are deposited into a pool, enabling trades on decentralized platforms.
- Fee Sharing: Trading fees collected from the pool are distributed among liquidity providers.
- Governance Token Rewards: Platforms often offer governance tokens as an additional incentive.
While this mechanism is straightforward, it introduces risks such as impermanent loss, particularly during market volatility.
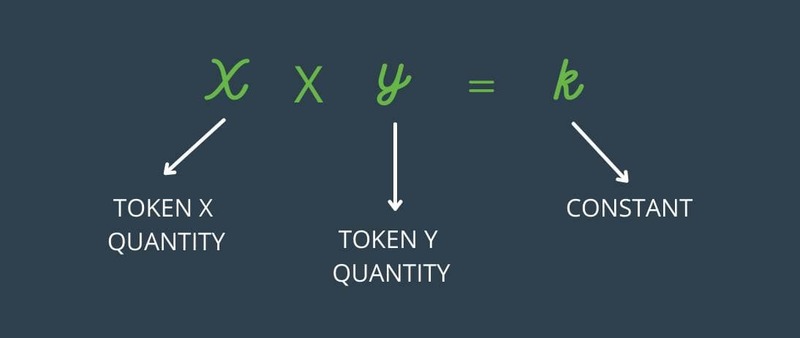
Impermanent Loss: A Core Risk in Yield Farming
Impermanent loss occurs when the value of tokens in a liquidity pool changes relative to their value at deposit. If token prices deviate significantly, the liquidity provider might suffer a loss compared to holding the tokens outright. These losses are termed “impermanent” because they only materialize when tokens are withdrawn. However, the volatile nature of crypto markets means this risk cannot be ignored.
APY vs APR in Yield Farming
When evaluating yield farming opportunities, you’ll encounter two key terms:
- APY (Annual Percentage Yield): Includes compounding interest.
- APR (Annual Percentage Rate): Reflects simple interest without compounding.
APY figures often seem more attractive but can be misleading. Manual compounding to achieve advertised APY levels is costly due to transaction fees. For practical purposes, most farmers rely on APR to gauge expected returns.
Leverage Yield Farming: Amplifying Risks and Rewards
Leverage yield farming involves borrowing assets to increase yield farming potential. While it can amplify returns, it also introduces significant risks, including liquidation during market downturns.
How to Yield Farm: A Step-by-Step Guide
Liquidity Providing
- Visit a decentralized exchange (DEX) like Raydium.
- Connect your wallet and navigate to the liquidity section.
- Select your preferred pool and deposit tokens.
Lending Assets
- Access money market platforms like AAVE.
- Choose an asset to lend and supply it to the protocol.
- Earn interest and optionally borrow against your collateral.
Staking Tokens
- Use platforms like Keplr to stake tokens.
- Choose a validator and delegate your tokens.
- Earn staking rewards over time while supporting network security.
Navigating Risks in Yield Farming
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Ensure protocols have undergone security audits.
- Rug Pulls: Be cautious of platforms with centralized control over funds.
- Impermanent Loss: Assess market conditions and token pair volatility.
- Liquidation Risks: Monitor collateral closely when borrowing assets.
Key Considerations for Safe Yield Farming
- Total Value Locked (TVL): A high TVL often signals a platform’s reliability.
- Source of Yield: Understand where returns are generated.
- Lock-Up Periods: Avoid overcommitting funds you might need during volatile market conditions.
Conclusion
Presents exciting opportunities for crypto enthusiasts to earn passive income, but it’s not without its pitfalls. By understanding the mechanisms, risks, and strategies involved, you can navigate this dynamic ecosystem with confidence. As with any investment, due diligence and risk management are crucial for success.
FAQs
What is yield farming in simple terms?
Involves locking up crypto assets in DeFi platforms to earn rewards such as transaction fees, interest, or governance tokens.
How can I start yield farming?
You can start by providing liquidity, lending assets, or staking tokens on platforms like AAVE, Uniswap, or Raydium.
What are the risks?
Key risks include impermanent loss, smart contract vulnerabilities, and liquidation risks when borrowing.
How is APY different from APR in yield farming?
APY includes compounding interest, while APR reflects simple interest without compounding.
What is impermanent loss?
Impermanent loss refers to the reduction in asset value in a liquidity pool due to price changes of the pooled tokens.
Are high yields always good in DeFi?
Not necessarily. High yields often come with high risks, such as inflationary tokens or volatile market conditions.















Leave a comment